With the development of information technology, customers can choose to use a virtual server VPS to be used as a separate server for the company’s needs. But now a new concept, and new technology is being used and brings better efficiency that is Cloud Smart. Articles What Is Cloud Smart? We will help you understand better.

Table of Contents
Definition of Cloud Smart
Along with the development of information technology today, individuals, organizations and businesses do not need to invest large costs to be able to own and use a Server server to serve office work, develop e-commerce, and application of information technology for business activities, commerce, and services, communication of the company.
Cloud Smart will provide customers with a virtual private server similar to VPS but developed and deployed based on cloud computing technology. So will inherit the features and outstanding advantages of this new technology that you will not get when using normal VPS.

Your Cloud Smart works on multiple physical Server connections. This gives you instant access to an unlimited supply of resources that are traditionally limited to a single physical server.
Your cost is determined by the number of Resource Nodes you choose including your CPU, RAM, storage space, and monthly bandwidth. Cloud Smart is fully customizable and can scale resources up or down to meet your usage needs.
Strategy for using Cloud Smart
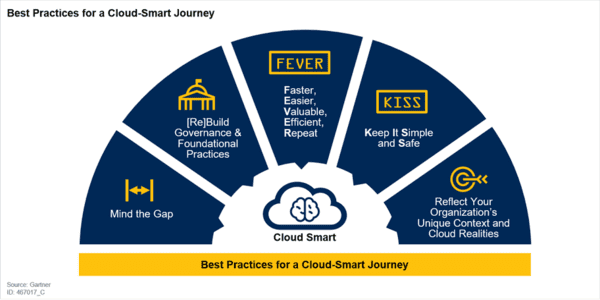
Smart Cloud Strategy, released in October 2018, is the second release of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) after the first OMB release called Cloud First in 2011. It is part of the Federal Government’s IT Modernization effort.
The Cloud First initiative states that the Federal Government must move to the Cloud but does not provide specific guidance on how to implement cloud adoption. The Cloud Smart Strategy provides additional guidance on security, procurement, and workforce skills needed to drive cloud adoption and deployment.
The Cloud Smart policy aims to accelerate the realization of value in cloud computing by requiring agencies to evaluate safe, secure cloud computing options before making any new investments. This policy is a key element of the government’s reform effort to achieve operational efficiency by adopting a shared service model.
Features and advantages of Cloud Smart
Expand quickly when needed, and downgrade Ram and CPU when you don’t need to use a lot of resources.
SSD storage system, bandwidth, and transmission up to several tens of Gbps.
Guaranteed 99.99% operation (temperature 22±1 degrees Celsius, UPS, backup power, explosion-proof).
The server is located in an international standard, professional and highly secure DataCenter, and we have Layer 7 and Layer 4 Anti DDos systems.
Full control and use of the free installed server, software, and operating system whenever you require it.
Allows administration remotely or directly at the Datacenter.
High-grade virus protection.
VXLAN technology creates independent virtual networks, Firewall two layers are layer 4 and layer 7.
Customers enjoy a variety of after-sales services.
Activate your Cloud Smart strategy
Deciding which apps are better in the cloud and which to stay on-premises is only half the battle for a Cloud Smart strategy. As business needs evolve, you need the flexibility to move data to the cloud (or vice versa).
Your team needs the flexibility to quickly migrate data to meet these changing needs.Rapid upgrades and migrations do not guarantee that your applications will perform as expected once they are in the cloud.
And refactoring applications can be too time-consuming and potentially risky. You can move data quickly and easily by managing data on-premises through a cloud data platform.
Because applications live on top of the Cloud Data Platform and not the underlying infrastructure, users get a consistent experience no matter where their data resides.
That means you can run mission-critical workloads that demand high performance, stability, and availability and still get the same experience as you use on-premises.
Cloud Smart is about moving all your applications to the cloud, starting with the most basic applications first.
But with a Cloud Smart strategy, you can have a more advanced strategy knowing that no matter how complex or important the application is, you can still bring it to the cloud using the cloud data platform.
How does Cloud Smart work?
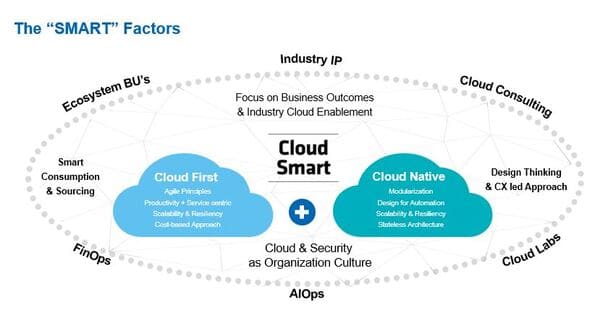
Cloud intelligence requires user teams to consider the broader implications and full benefits of cloud adoption.

This includes consideration of people, processes, technology, modern sourcing and business interfaces. These factors include:
Agility: Large-scale adoption of DevOps and containerization will likely require a revised IT operating model, as well as more agile development and deployment processes.
The flexibility these technologies offer means that businesses can have an idea for a new way of doing business and have a better idea of what to do and operate.
Service management: You also need to consider the overall service management structure of your business.
Because if you’ve migrated from a data center owned asset to a private or public cloud, for example. The way you manage major incidents also needs to change.
Tools and Instruments: Tools need to change, too, because you’ve moved from managing physical assets like servers or network devices to apps.
The data workflow is using the public cloud provider’s virtualization service. This requires modern tools and equipment to allow you to view IT workflows from start to finish.
Tool products such as application performance management measure end-to-end processes, allowing insight into what’s happening in the cloud. This becomes more important than ever with the whole product approach of the industrial cloud.
Considerations when using the Cloud Smart
You need to understand your business strategy first, then look for smart opportunities in the cloud to leverage new capabilities to ensure your business adopts and accelerates the strategy.
Think about your time. Plan for phases 1 and 2 of using the cloud. Do not rush to use, but carefully evaluate the workload and usage needs of the system.
Consider decommissioning business application replacement programs. For example, it is better to remove the on-premises business applications and instead switch to infrastructure or platform as a service (IaaS and PaaS).
Create a plan for all phases, including post-migration optimization and industry cloud adoption.
Take into account the achievable carbon reduction benefits and track those benefits as part of the company’s ESG report.
Conclusion
Moving to a cloud-smart approach enables organizations to take advantage of technological developments. This increases flexibility and reduces costs. That way businesses will harness the value of the cloud, ensuring their investments stand the test of time.
